The amount of data available today represents an unprecedented opportunity for marketers. Discovering patterns in data collected through website traffic, lead generation forms, email marketing, in-app behavior, or social media (just to name a few), gives marketers a glimpse into the mind of a consumer like never before.
We know this, and we know that properly analyzing this data is the key to unleashing its awesome potential. However, there remains a discrepancy between the awareness of the importance of analytics and the ability of marketers to utilize it correctly in their campaigns.
In the following, we’ll discuss three simple things: The power of data/analytics in marketing, the most common problems with data analytics, and the consequences of utilizing bad data. Plus a few solutions and conclusions.
The power of data
As the author and consultant Geoffrey Moore put it: “without data analytics, companies are blind and deaf, wandering around like deer on the high way.” This may be a bit hyperbolic but it doesn’t miss the mark by much.
Drawing proper conclusions from available data can shape the future of sales and helps marketers adjust their campaigns to make them more effective. The ways data can help marketers are essentially endless. A few examples:
Segmentation: simply breaking down customers into meaningful demographic groups such as age, location, gender, occupation, etc. This allows you to better tailor your marketing & SEO efforts.
Identification: see which specific types of content moves buyers further down the sales funnel, and what effects it may have on conversion rates, and other metrics.
Evaluation: checking the success of a campaign by measuring performance specifics (e.g., blogging versus social media versus channel communications).
Understanding behavior: looking at customer data can allow marketers to better understand why (and for what) people use their products. Western Union leveraged data by understanding that many of their customers used their service for rent and tuition (and often outside the United States). They marketed accordingly.
The above barely scratches the surface of what can be done with data. Also, there’s still a relatively high percentage of marketers who don’t put enough emphasis in the correct areas when it comes to data analysis.
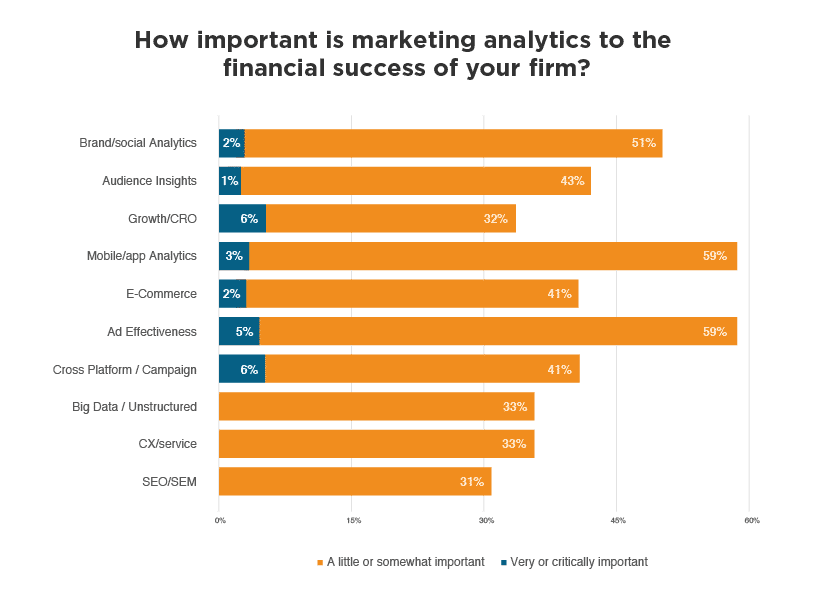
Source: Venture Beat
The study by Venture Beat revealed that marketers consider big data analytics, plus CX/service and SEO/SEM analytics critical to the financial success of various companies (over 60%), compared to brand/social analytics, mobile/app analytics, and ad effectiveness analytics which are considerably less important.
What is surprising here is that the three categories of analytics which scored the lowest could arguably be of most use for marketers. Data taken directly from customer behavior on mobile apps or social media provides relatively intimate data for marketers to create highly-personalized lead nurturing.
Personalized lead nurturing is one of the most effective ways to retain customers and generate sales. In fact, businesses focused on lead nurturing generate on average 50% more sales-ready leads at 33% lower cost.
According to MarketingSherpa Marketers neglecting the development of personalized lead nurturing can expect as many as 79% fewer of their leads to convert.
Common problems with data analytics
If you look under the hood, the problem with analytics is much broader than marketers not focusing in the correct ways. As the graph below shows up to 45% of marketers don’t validate their data for quality and accuracy.
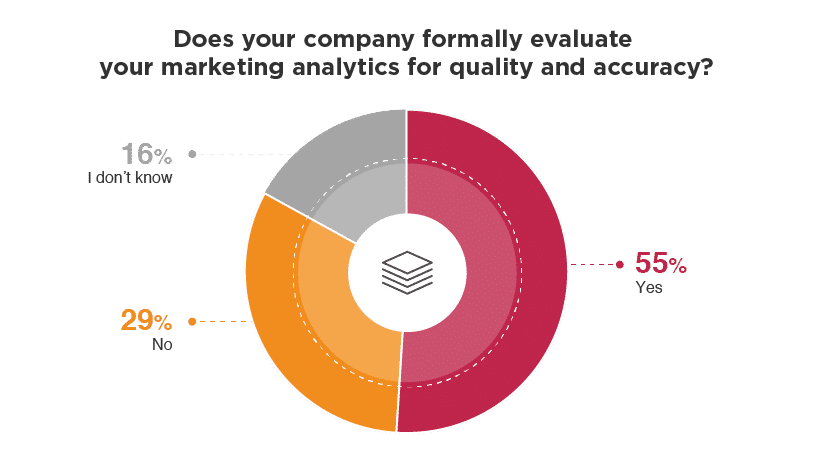
Source: Venture Beat
According to Demand Gen Report, over 62% of companies use prospect data that is incomplete or invalid. Furthermore, Dun & Bradstreet’s report found that out of 223M records analyzed more than 66% were missing revenue and industry data.
Data incompleteness should be particularly alarming because it essentially stalls marketing operations by preventing marketers from extending their contacts base and building the proper image of the customer.
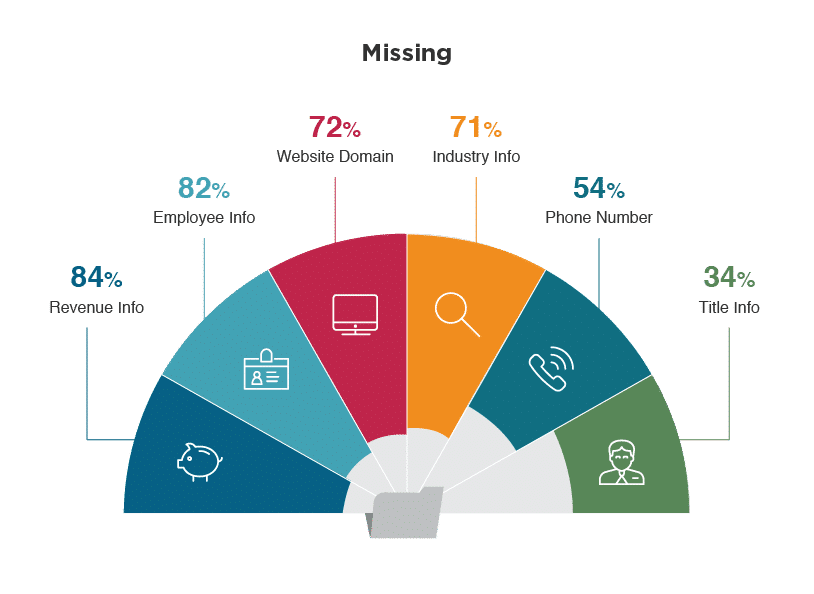
Source: dun&bradstreet
Still poor data quality makes only 23% of all issues marketers encounter with it. Among others, there is also: inappropriate data management and maintenance, and lack of unified data storage and quality control.
In the end, marketers must spend a lot of their time arranging and sorting out the data instead of working with it, drawing the picture of the buyer and refining their efforts. It’s essentially a problem of scale. There is so much data, and so much of it is outdated or invalid that marketers often struggle to extract insights or acquire anything meaningful.
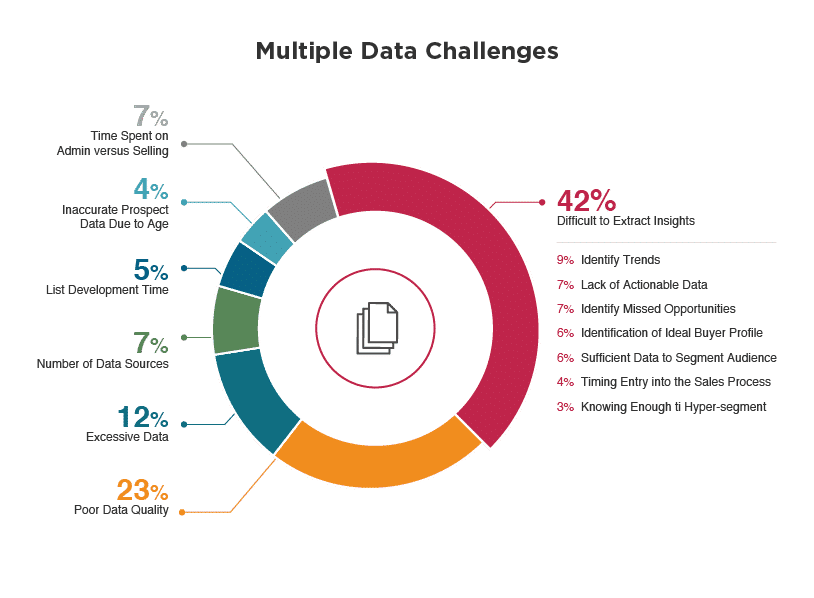
Source: Avention
The good news is that there are more than a couple useful tools to help you circumnavigate these problems.
Bad data, big problems
Ovum Research estimated that poor data quality can cost companies 30% of revenue or more annually.
Dirty or bad data can disrupt the entire revenue flow of an organization, and with a strong need to fill the funnel, bad data is seeping into our marketing & CRM systems. This can be on the transactional level (micro) or the organizational level (macro).
A brief rundown on some of the effects of bad data:
- Mistakes in product/mail deliveries
- Reduced customer satisfaction and retention rates
- Elevated churn rate
- Distortion of success metrics
- A higher failure rate with marketing initiatives
- A spike in spam counts and customer un-subscriptions
- Negative blowback on social media
These are just to name a few, and there are a host of other downstream impacts from the utilization of bad data.
Solution and conclusion
Marketers should ensure their data is evaluated for accuracy. You need accurate, up to date data that is clean. It’s that simple.
Follow-up searches, cross checks and data cleansing processes are all crucial to the well-being of today’s marketing. In a word, diligence.
However, it’s not only up to marketers to care about data quality. To leverage data analytics business owners should start by investing in proper data management and governance. This can be in the form of people or tools.
Cleaning, organizing and being diligent all can have an enormous impact on the ROI of your data analytics. Only after this foundation is laid can some of the pitfalls of bad data be laid to rest.

